Developing an Effective Dementia Care Plan: A Comprehensive Guide for Improved Quality of Life
Developing an Effective Dementia Care Plan: A Comprehensive Guide for Improved Quality of Life
Caring for loved ones with dementia can be a challenging and deeply emotional journey. As the disease progresses, individuals with dementia require specialized care and assistance tailored to their unique needs. This is where an effective dementia care plan can make a world of difference.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key components of developing a dementia care plan that promotes improved quality of life for both the individual with dementia and their caregivers. From understanding the stages of dementia to implementing person-centered care, we will provide valuable insights and practical strategies to ensure the highest level of care and support.
Drawing on the latest research and expert advice, this guide will delve into crucial aspects such as medication management, communication techniques, activity planning, and creating a safe environment. With our step-by-step approach, caregivers will gain the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the challenges of dementia care with confidence and compassion.
Join us as we embark on this journey of enhancing the lives of those living with dementia and empowering their caregivers to provide the best possible care.
Understanding dementia and its impact on quality of life
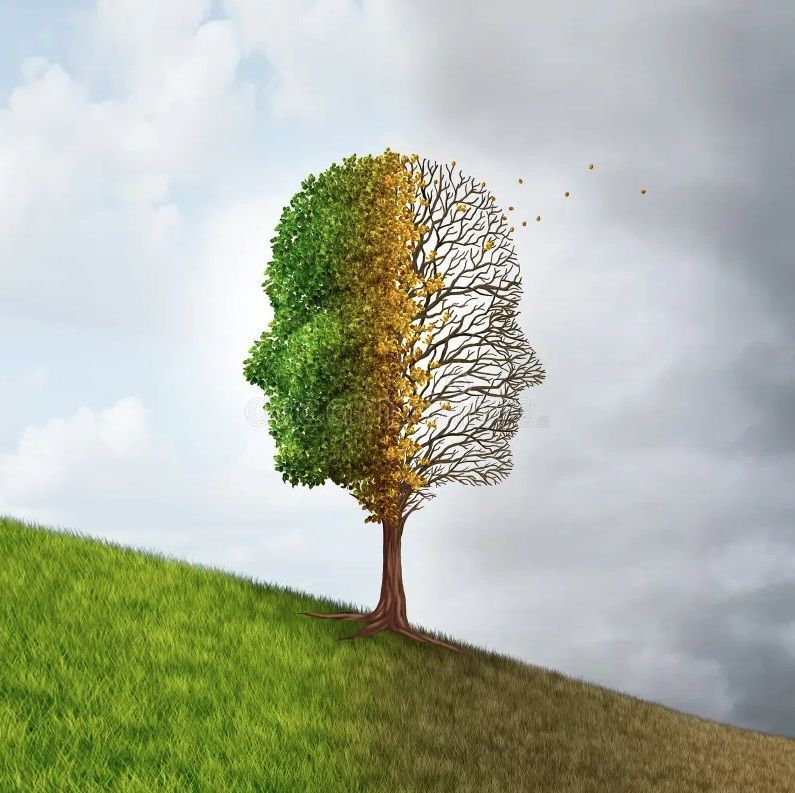
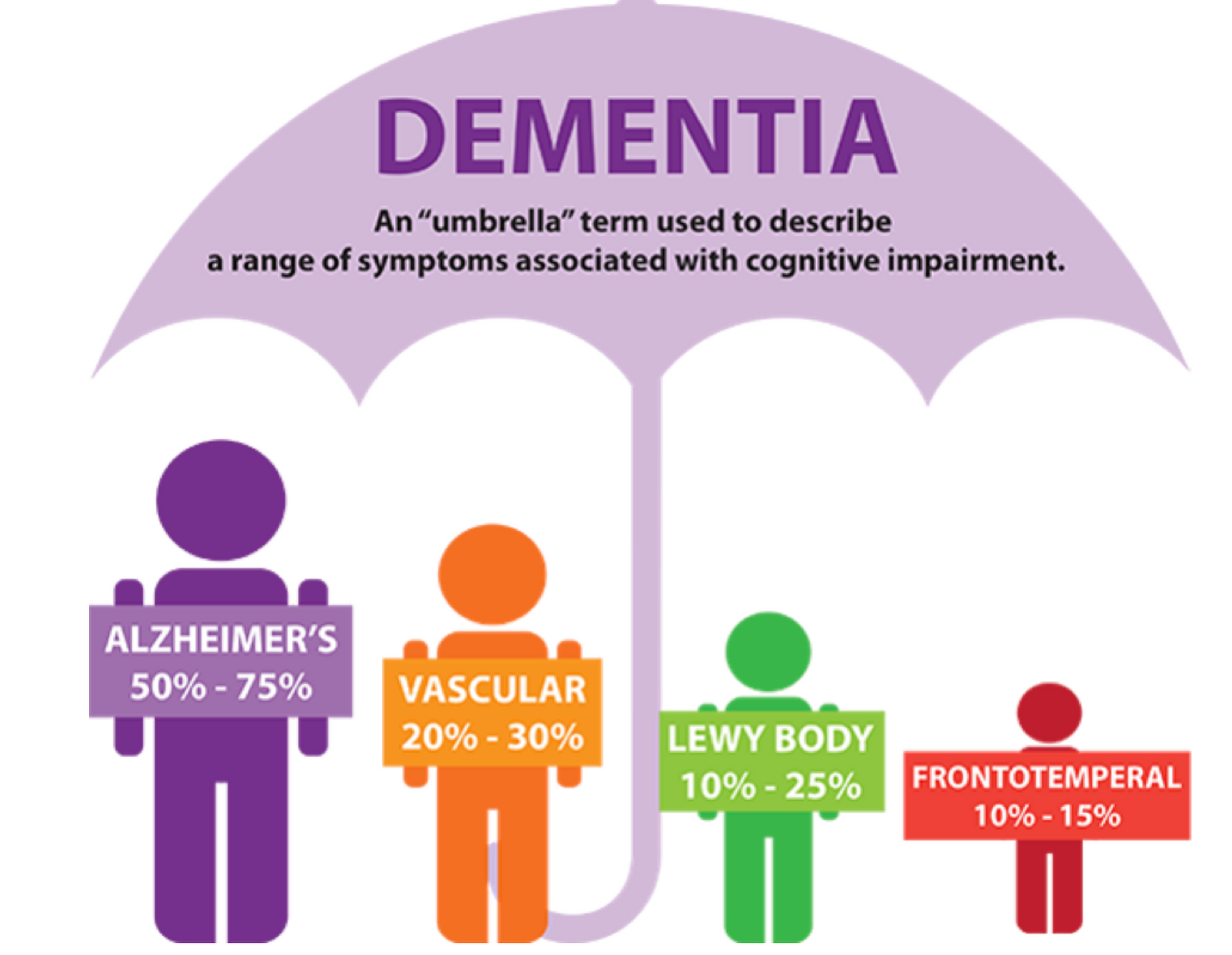
Dementia is not a single disease but a term that encompasses a variety of symptoms related to cognitive decline, affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities. It represents a significant challenge not just for those diagnosed but for their families and caregivers as well. As the disease progresses, individuals may face difficulties in performing daily activities, leading to a gradual loss of independence. This decline can severely affect their quality of life, making it essential to understand the various stages of dementia and how they impact both the individual and their loved ones.
The early stages of dementia may involve mild memory loss or confusion. However, as the condition advances, individuals may struggle with recognizing familiar faces, understanding language, or managing their emotions. This cognitive decline can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and anxiety, which further diminishes their overall quality of life. Moreover, caregivers often experience emotional strain, which can affect their ability to provide adequate support. Thus, grasping the extent of dementia's impact is crucial for developing effective care strategies.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of dementia is vital for creating a supportive environment. It is important to recognize that each individual experiences dementia differently, with unique strengths and challenges. This variability means that a one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective. Instead, a tailored care plan focused on enhancing quality of life should address specific needs, preferences, and abilities. By fostering an understanding of dementia’s impact, caregivers can create a more empathetic and supportive atmosphere, which is essential for promoting dignity and respect for the individual.
Importance of a comprehensive dementia care plan
A comprehensive dementia care plan is essential for ensuring that individuals receive the tailored care they need as their condition evolves. Such a plan serves as a roadmap for caregivers, outlining specific strategies and interventions designed to enhance the quality of life for those living with dementia. By establishing clear goals and objectives, caregivers can provide more effective and focused support, leading to better outcomes for both the individual and their families.
The importance of a comprehensive care plan lies in its ability to address the many dimensions of dementia care. It encompasses not only medical needs but also emotional, social, and environmental factors that contribute to the overall well-being of the individual. By taking a holistic approach, caregivers can create a more rounded support system that considers the unique challenges faced by those with dementia. This comprehensive framework helps ensure that no aspect of care is overlooked, allowing for a better quality of life.
Moreover, an effective care plan facilitates communication among all parties involved, including healthcare professionals, family members, and the patient. A well-documented plan ensures everyone is on the same page regarding the individual’s care needs and preferences, which can significantly reduce misunderstandings and conflicts. By fostering collaboration and open dialogue, a comprehensive care plan not only enhances the quality of care but also empowers caregivers and families to provide the best possible support for their loved ones.
Assessing the individual needs of a person with dementia
Assessing the individual needs of a person with dementia is a critical first step in developing an effective care plan. This assessment involves gathering information about the individual's medical history, cognitive abilities, emotional state, and personal preferences. Understanding these elements allows caregivers to tailor their approach and ensure that the care provided is both appropriate and meaningful. Individual assessments should be ongoing, as dementia is a progressive condition, and needs may change over time.
In addition to medical assessments, caregivers should consider the individual's social history, including their interests, hobbies, and cultural background. Such information can provide insights into how to engage the person in activities that they find enjoyable and meaningful. For example, if an individual has a passion for music, incorporating music therapy into their daily routine can provide comfort and joy, enhancing their overall quality of life. Understanding personal history allows caregivers to create a more personalized and engaging care experience.
Furthermore, assessing the individual’s environment is crucial. The physical space where a person with dementia resides should be safe and conducive to their well-being. This includes removing potential hazards, ensuring adequate lighting, and creating a familiar setting that minimizes confusion. By evaluating both the individual’s needs and their environment, caregivers can develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses all aspects of the person’s life, ultimately promoting dignity, comfort, and security.
Creating a person-centered care approach
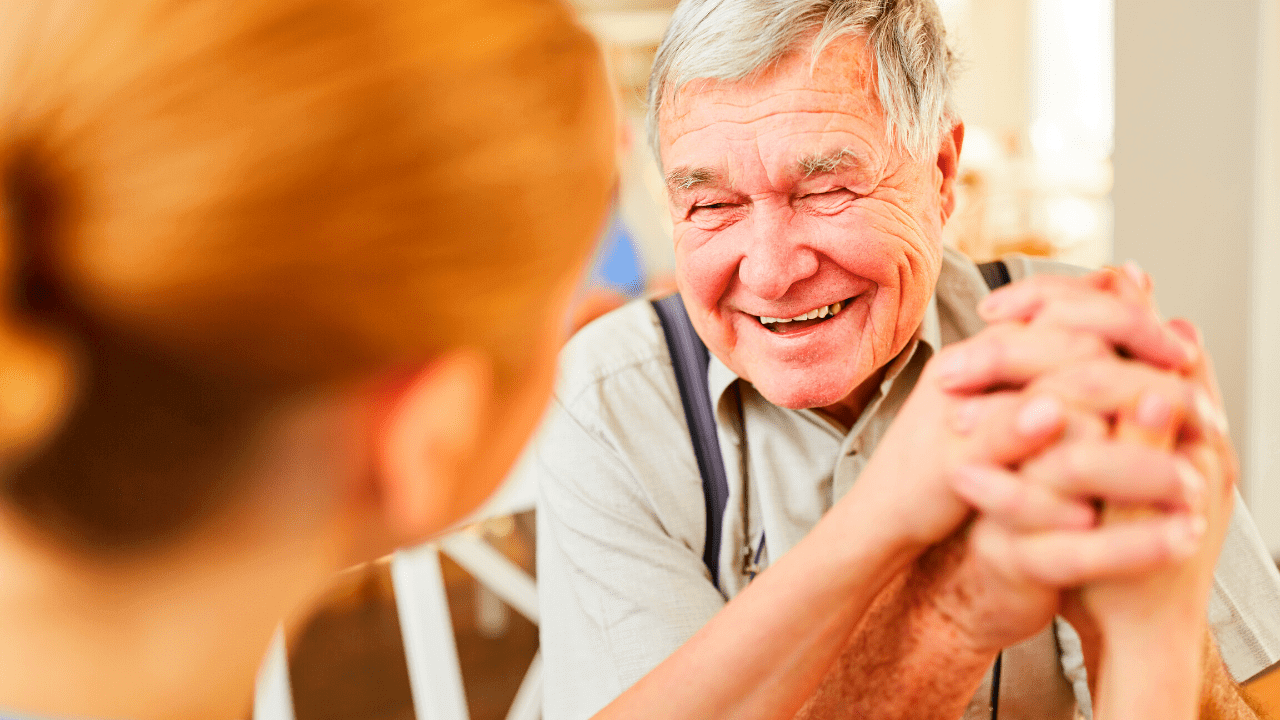
A person-centered care approach is fundamental to providing effective dementia care. This methodology emphasizes the individuality of each person, recognizing that their experiences, preferences, and needs should guide the care provided. By focusing on the person rather than the disease, caregivers can create a more supportive and respectful environment that acknowledges the inherent dignity of the individual. This approach fosters a sense of agency and involvement for the person with dementia, making them feel valued and understood.
Implementing a person-centered approach requires active engagement with the individual. Caregivers should take the time to listen to their loved ones, ask questions about their preferences, and involve them in decision-making processes related to their care. This may include choosing daily activities, meals, or even care routines. Empowering individuals to express their desires and preferences contributes to their overall sense of well-being and satisfaction, which can positively influence their emotional and cognitive health.
Moreover, person-centered care extends beyond just the individual with dementia; it also involves family members and caregivers. Communication and collaboration among all parties are essential in ensuring that the care plan aligns with the individual’s values and goals. By fostering an environment of mutual respect and understanding, caregivers can create a supportive network that enhances the quality of life for everyone involved. Ultimately, adopting a person-centered approach can transform the caregiving experience into one that is more compassionate, fulfilling, and effective.
Building a supportive environment for individuals with dementia
Creating a supportive environment for individuals with dementia is crucial in promoting their safety, comfort, and overall well-being. The physical space in which they live should be designed to minimize confusion and enhance their ability to navigate their surroundings. This includes decluttering spaces, using clear signage, and ensuring that essential items are easily accessible. A well-organized environment can significantly reduce anxiety and frustration, allowing individuals to maintain some degree of independence.
In addition to the physical aspects, emotional support plays a vital role in creating a nurturing environment. Caregivers should strive to build a warm and welcoming atmosphere that fosters trust and connection. This can be achieved through consistent routines, familiar objects, and meaningful interactions. Engaging in conversations, sharing stories, and participating in activities that the individual enjoys can help strengthen the emotional bond between caregiver and recipient, enhancing the overall caregiving experience.
Furthermore, incorporating elements of nature and sensory stimulation can greatly benefit individuals with dementia. Research has shown that exposure to natural light, greenery, and soothing sounds can improve mood and cognitive function. Caregivers can create a sensory-rich environment by introducing plants, artwork, and calming music. This holistic approach not only promotes a sense of peace and tranquility but also encourages engagement and interaction, ultimately supporting the individual’s quality of life.
Implementing effective communication strategies
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful dementia care. As cognitive abilities decline, individuals may struggle to express themselves or understand what others are saying. Caregivers must adapt their communication styles to meet the needs of the person with dementia. This involves using clear, simple language, maintaining eye contact, and being patient during conversations. By creating an environment that encourages open dialogue, caregivers can foster a sense of connection and understanding, which is vital for emotional well-being.
Non-verbal communication also plays a significant role in dementia care. Caregivers should be attuned to body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice, as these can convey important messages. For instance, a gentle touch or a reassuring smile can provide comfort and reassurance to individuals who may feel anxious or confused. Additionally, caregivers can employ visual aids, such as pictures or written cues, to enhance understanding and facilitate communication. These strategies can help bridge the gap between the caregiver and the individual, making interactions more meaningful and effective.
Moreover, active listening is essential in fostering effective communication. Caregivers should allow individuals the time to express themselves, even if it takes longer than usual. Acknowledging their feelings and validating their experiences can build trust and confidence in the caregiver. By creating a safe and supportive space for communication, caregivers can help individuals with dementia feel heard and understood, ultimately improving their quality of life and emotional health.
Providing appropriate cognitive stimulation and engagement activities
Cognitive stimulation and engagement activities are vital components of dementia care that can significantly enhance quality of life. Research has shown that engaging individuals in mentally stimulating tasks can help slow cognitive decline and improve mood. Activities should be tailored to the individual’s interests and abilities, fostering a sense of accomplishment and enjoyment. This can include puzzles, arts and crafts, music therapy, or even simple conversation about familiar topics.
In addition to individualized activities, social engagement is equally important. Group activities can provide individuals with the opportunity to connect with others, share experiences, and participate in meaningful interactions. Caregivers can facilitate social engagement by organizing group games, outings, or community events that allow individuals to socialize in a supportive environment. These interactions can combat feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common among those living with dementia.
Furthermore, incorporating routine and structure into daily activities can provide a sense of stability for individuals with dementia. Establishing a schedule that includes a mix of cognitive, physical, and social activities can help create a balanced routine that promotes overall well-being. Caregivers should be flexible and attentive to the individual’s energy levels and preferences, adjusting activities as needed to ensure that they remain engaged and fulfilled. By prioritizing cognitive stimulation and engagement, caregivers can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with dementia.
Addressing behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD)
Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) are common and can significantly impact the quality of life for both individuals and caregivers. Symptoms may include agitation, depression, anxiety, and hallucinations, which can create challenging situations in caregiving. Understanding the root causes of these behaviors is essential for developing effective strategies to manage them. Often, BPSD can be triggered by unmet needs, changes in the environment, or even medical issues, making it crucial for caregivers to remain observant and empathetic.
One effective approach to managing BPSD is through non-pharmacological interventions. These strategies focus on modifying the environment, providing appropriate activities, and offering emotional support. Techniques such as validation therapy, which involves acknowledging and validating the individual’s feelings and experiences, can help reduce agitation and promote a sense of security. Additionally, creating a calm and predictable environment can minimize triggers that may lead to distressing behaviors.
When non-pharmacological approaches are insufficient, caregivers may need to consult healthcare professionals to explore appropriate medical interventions. Medication can sometimes be necessary to manage severe symptoms effectively, but it should be approached with caution and as a last resort. Regular monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers are crucial to ensure that any interventions align with the individual’s overall care plan. By addressing BPSD thoughtfully and comprehensively, caregivers can enhance the well-being of individuals with dementia and create a more harmonious caregiving experience.
Integrating medical and non-medical interventions in the care plan
Integrating medical and non-medical interventions is essential for creating a comprehensive dementia care plan that addresses the multifaceted needs of individuals. Medical interventions typically involve monitoring and managing health conditions, medication management, and regular consultations with healthcare professionals. These aspects are crucial in ensuring that any underlying health issues are addressed and that medications are effectively managing symptoms without causing adverse effects.
Non-medical interventions, on the other hand, focus on enhancing the emotional, social, and cognitive well-being of the individual. These can include engaging in meaningful activities, fostering social connections, and creating a supportive environment. By incorporating both medical and non-medical approaches, caregivers can provide holistic care that addresses the various dimensions of dementia. This integrated strategy not only improves the individual’s quality of life but also supports their overall health and well-being.
Regular evaluation of both medical and non-medical interventions is crucial in ensuring their effectiveness. Caregivers should continually assess the individual’s response to treatments and activities, making adjustments as needed. This dynamic approach allows caregivers to remain flexible and responsive to the changing needs of the individual. By fostering collaboration among healthcare providers, family members, and caregivers, a comprehensive care plan can evolve to meet the unique challenges posed by dementia, ultimately promoting a better quality of life for those affected.
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the dementia care plan
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of a dementia care plan is a critical component of ensuring that it meets the unique needs of the individual. Regular assessments allow caregivers to gauge how well the implemented strategies are working and identify areas that may require adjustment. This ongoing evaluation process should include feedback from the individual, family members, and healthcare professionals to gain a comprehensive understanding of the care plan’s impact.
Key indicators for monitoring effectiveness may include changes in cognitive function, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. Caregivers should document any observed changes or challenges, providing a clear record that can guide future decisions. Additionally, maintaining open lines of communication with all parties involved in the individual’s care fosters collaboration and ensures that everyone is informed about the plan's progress and any necessary modifications.
Ultimately, the goal of monitoring and evaluating the care plan is to enhance the quality of life for the individual with dementia. By being proactive and responsive to their evolving needs, caregivers can create a supportive and nurturing environment that promotes dignity and respect. Regular evaluation not only strengthens the care provided but also empowers caregivers to adapt and respond to the challenges that dementia presents, ensuring that individuals receive the best possible support throughout their journey.