Recognizing and Preventing Cognitive Decline: Tips, Strategies, and Evidence-Based Solutions
In this fast-paced world, cognitive decline has become a growing concern for many people. The ability to remember, learn, and think clearly is essential for our daily functioning, and it's crucial to take proactive steps to prevent cognitive decline. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the tips, strategies, and evidence-based solutions to keep your brain sharp and healthy.
From lifestyle changes and diet modifications to mental exercises and brain-boosting supplements, we'll explore a wide range of approaches that can help preserve cognitive function. We'll delve into the latest research and expert insights to provide you with practical advice that you can incorporate into your daily routine.
Whether you're in your 30s or your 60s, it's never too early or too late to start taking care of your brain health. By following the recommendations in this guide, you'll improve your cognitive abilities, enhance your quality of life, and reduce the risk of cognitive decline. So, let's embark on this journey together and unlock the secrets to maintaining a healthy and vibrant mind.
Understanding the Causes of Cognitive Decline
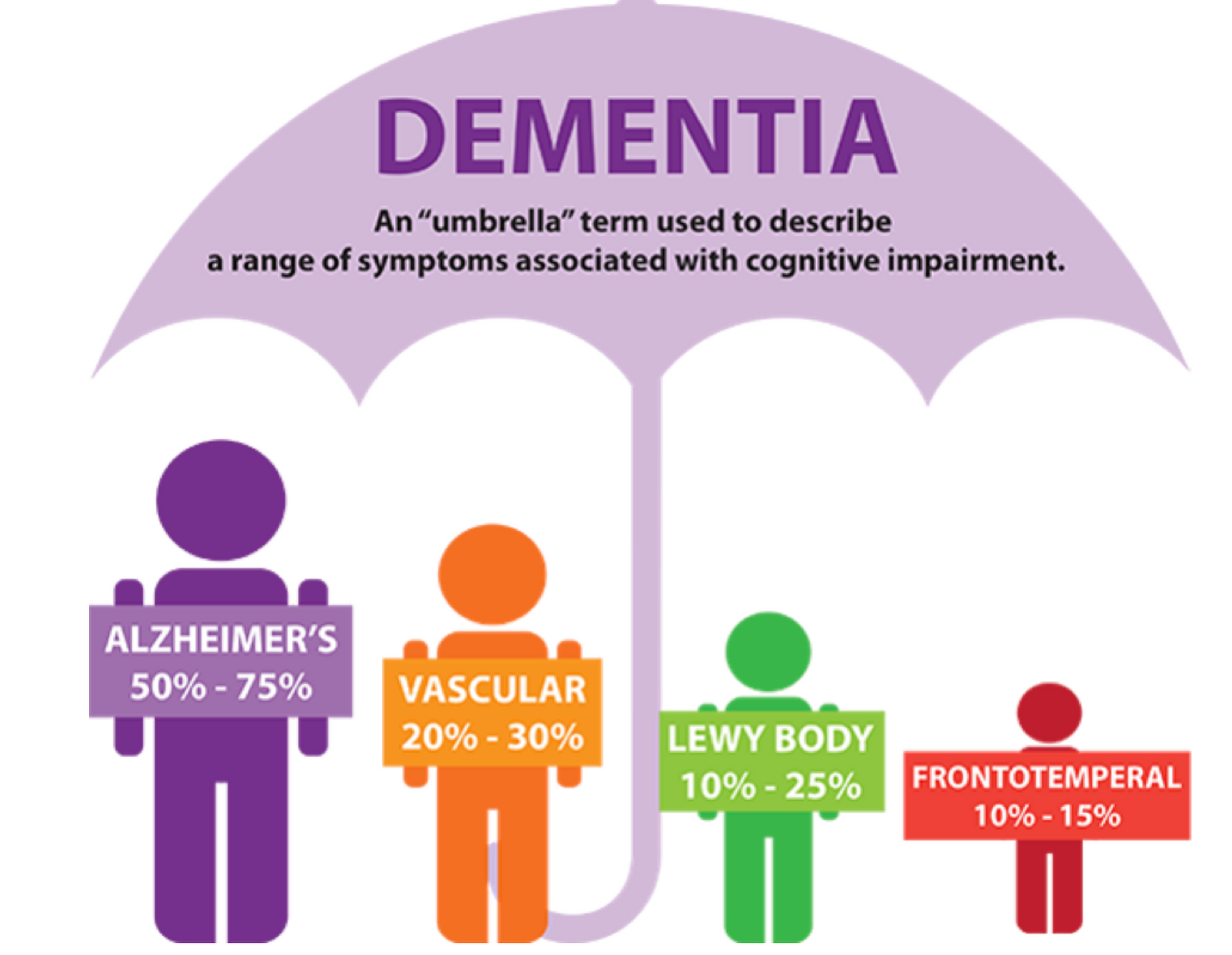
Cognitive decline can be attributed to a variety of factors that affect brain health over time. One of the primary causes is the natural aging process. As individuals age, brain cells may begin to lose their ability to communicate effectively, leading to slower processing speeds and diminished memory capabilities. This age-related decline can be exacerbated by the presence of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, which contribute to significant changes in brain structure and function. Research indicates that these diseases can disrupt synaptic connections, leading to the loss of cognitive abilities that are crucial for daily living.
Another significant contributor to cognitive decline is the impact of chronic medical conditions. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases can impair blood flow to the brain, resulting in cognitive deficits. These health issues can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are detrimental to brain cells. Moreover, lifestyle habits associated with these conditions, including poor dietary choices and lack of physical activity, can further compound the risk of cognitive decline. Addressing these chronic conditions through appropriate medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments can be essential in mitigating their effects on cognitive health.
Environmental factors also play a critical role in cognitive decline. Exposure to pollutants, toxins, and even social isolation can lead to cognitive impairments. Studies have shown that individuals living in areas with high levels of air pollution may experience accelerated cognitive decline compared to those in cleaner environments. Additionally, social engagement is vital for maintaining cognitive function. A lack of social interaction can increase feelings of loneliness and depression, both of which are linked to cognitive deterioration. Understanding these multifaceted causes can help individuals take proactive measures to safeguard their cognitive health.
Signs and Symptoms of Cognitive Decline
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of cognitive decline is crucial for timely intervention. Common indicators include memory loss, particularly the inability to recall recent events or conversations. Individuals may find themselves frequently misplacing items or struggling to remember names and faces. This type of forgetfulness, while normal to some extent, can become concerning when it begins to interfere with daily activities. Furthermore, difficulties in planning or organizing tasks can signal cognitive changes, making it challenging for individuals to manage their responsibilities effectively.
Another symptom is the decline in language skills, which may manifest as difficulty in finding the right words during conversations. People experiencing cognitive decline may also notice a reduction in their ability to follow or engage in discussions, leading to frustration and withdrawal from social interactions. Additionally, altered judgment and reasoning can be significant signs; individuals may struggle to make sound decisions or may exhibit poor judgment in everyday situations, such as managing finances or understanding safety instructions.
Mood changes can also accompany cognitive decline, often resulting in increased irritability, anxiety, or depression. These emotional shifts can further complicate the cognitive issues, as feelings of sadness or frustration can lead to withdrawal from activities and social situations that were once enjoyable. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for better management and intervention strategies, making it essential for individuals and their families to be aware of these changes and seek help when necessary.
The Importance of Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection of cognitive decline is paramount in implementing effective prevention strategies. Identifying cognitive changes at an early stage can lead to timely interventions that may slow the progression of decline or even reverse some symptoms. Regular cognitive assessments, whether through formal testing or self-evaluation, can help individuals and healthcare providers monitor changes over time. Being proactive about cognitive health encourages individuals to seek help when they notice concerning signs, allowing for immediate action to be taken.
Prevention strategies are most effective when started early in life. Engaging in a brain-healthy lifestyle can significantly lower the risk of cognitive decline later in life. This includes adopting healthy dietary habits, participating in regular physical exercise, and fostering social connections. By making these lifestyle choices, individuals can build cognitive resilience, equipping their brains to withstand age-related changes. Additionally, pursuing lifelong learning through educational opportunities and mental challenges can stimulate brain health and encourage neural plasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself.
Moreover, early detection and prevention not only benefit cognitive health but also improve overall quality of life. Individuals who take proactive steps to support their cognitive function often experience enhanced emotional well-being and greater independence as they age. This holistic approach fosters a sense of agency, empowering individuals to take control of their health and longevity. By focusing on prevention and early detection, we can combat cognitive decline and promote a vibrant, fulfilling life well into our later years.
Lifestyle Factors That Contribute to Cognitive Health
Lifestyle factors play a pivotal role in maintaining cognitive health throughout life. One of the most influential is physical activity. Engaging in regular exercise is associated with improved blood flow to the brain, which can enhance cognitive function and protect against decline. Exercise stimulates the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and survival of neurons. Incorporating a mix of aerobic, strength training, and balance exercises into daily routines can significantly benefit brain health and overall well-being.
Sleep also plays a critical role in cognitive function. Quality sleep is essential for memory consolidation and learning. During sleep, the brain processes and organizes information acquired during the day, helping to strengthen neural connections. Chronic sleep deprivation, on the other hand, can lead to cognitive impairments, increased stress levels, and a higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a calming bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can help individuals prioritize and achieve restorative sleep.
Social engagement is another lifestyle factor that influences cognitive health. Maintaining strong social connections and participating in community activities can enhance cognitive resilience. Studies have shown that individuals with rich social lives tend to experience slower cognitive decline compared to those who are socially isolated. Engaging in meaningful conversations, joining clubs, or volunteering can provide mental stimulation while fostering a supportive network. Building and maintaining these connections can create a protective effect for cognitive health, making social engagement an essential component of a holistic approach to preventing cognitive decline.
Nutrition and Cognitive Health
Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting cognitive health and preventing decline. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal brain function. The Mediterranean diet, for example, emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, fish, and healthy fats, particularly olive oil. Research has shown that adhering to this diet is associated with a lower risk of cognitive decline. The inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and nuts, has been linked to improved memory and cognitive function as they play a vital role in maintaining neuronal health.
Certain nutrients are particularly beneficial for brain health. Antioxidants, found in berries, dark chocolate, and leafy greens, help combat oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells. Additionally, vitamins such as B6, B12, and folate are essential for maintaining healthy brain function and preventing cognitive decline. These vitamins support neurotransmitter synthesis and reduce homocysteine levels, which have been associated with cognitive impairment. Including a variety of nutrient-dense foods in the diet ensures that the brain receives the necessary support to function optimally.
It is also important to limit the intake of processed foods, added sugars, and saturated fats, which can negatively impact cognitive health. Diets high in these elements have been linked to inflammation and cognitive decline. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and minimizing harmful dietary components, individuals can create an environment that supports long-term brain health. Maintaining a healthy diet not only enhances cognitive function but also contributes to overall physical health, creating a virtuous cycle that promotes well-being.
Physical Exercise and Cognitive Health
Physical exercise is a powerful tool for enhancing cognitive health and preventing decline. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to improve memory, attention, and executive function. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen that support neuronal health. Moreover, physical activity promotes neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus, an area critical for learning and memory. This biological response to exercise highlights the importance of movement in maintaining cognitive vitality.
Different forms of exercise can benefit cognitive health in various ways. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, running, or swimming, are particularly effective in boosting brain function. These activities elevate heart rate and improve cardiovascular health, which is closely linked to cognitive performance. Strength training also plays a role; studies have indicated that resistance training can enhance cognitive abilities, especially in older adults. Additionally, activities that require coordination and mental engagement, such as dance or martial arts, can provide unique cognitive benefits by challenging the brain and body simultaneously.
Incorporating exercise into daily routines doesn't require lengthy sessions at the gym. Finding enjoyable physical activities and integrating them into everyday life can lead to sustainable habits. Short walks, gardening, or playing with pets can all contribute to active lifestyles. Setting achievable goals and tracking progress can also help individuals stay motivated. By prioritizing physical exercise, individuals can invest in their cognitive health, fostering a sharper mind and a more resilient brain as they age.
Mental and Social Engagement for Cognitive Health
Mental stimulation is vital for preserving cognitive function and preventing decline. Engaging in intellectually challenging activities can strengthen neural connections and promote cognitive resilience. Activities such as puzzles, reading, playing musical instruments, or learning a new language stimulate the brain and encourage lifelong learning. Research suggests that individuals who consistently engage in mentally stimulating activities throughout their lives tend to have a lower risk of cognitive decline. By making a habit of challenging the mind, individuals can enhance their cognitive abilities and keep their brains active.
Social engagement is equally important for cognitive health. Interacting with others provides mental stimulation and emotional support, both of which are essential for brain health. Participating in group activities, joining clubs, or volunteering can foster connections that promote cognitive vitality. Social interactions challenge individuals to think critically, recall memories, and engage in meaningful conversations, all of which stimulate the brain. Moreover, social engagement can help combat feelings of loneliness and depression, which are detrimental to cognitive health.
Combining mental and social engagement can create a powerful synergy for cognitive well-being. For instance, participating in book clubs or discussion groups not only provides intellectual stimulation but also fosters social connections. Group activities that involve teamwork or collaboration can enhance cognitive function while promoting a sense of belonging. By prioritizing both mental and social engagement, individuals can create a comprehensive approach to maintaining cognitive health and preventing decline, ensuring their minds remain vibrant and active throughout life.
Strategies for Preventing Cognitive Decline
Preventing cognitive decline involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses various strategies. One of the most effective ways to promote brain health is through lifestyle changes, including adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical exercise, and prioritizing sleep. Creating a daily routine that incorporates these elements can significantly enhance cognitive function and reduce the risk of decline. Setting specific, achievable goals can help individuals stay motivated and accountable in their journey towards better cognitive health.
In addition to lifestyle changes, mental exercises and brain training can play a crucial role in preventing cognitive decline. Utilizing brain-training apps, participating in memory games, or engaging in activities that challenge the mind can strengthen cognitive abilities. Research has shown that cognitive training can result in improvements in memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Furthermore, regularly challenging oneself with new skills or hobbies can create new neural pathways, supporting lifelong cognitive health.
Social engagement is another vital strategy for preventing cognitive decline. Building and maintaining strong social connections can provide emotional support and mental stimulation. Engaging in community activities, volunteering, or simply spending time with family and friends can help foster these connections. Encouraging social interactions and participation in group activities can create a supportive environment that promotes cognitive resilience. By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their cognitive health and reducing the risk of decline.
The Role of Medical Interventions in Preventing Cognitive Decline
While lifestyle changes and preventive strategies are essential, the role of medical interventions in preventing cognitive decline cannot be overlooked. Regular medical check-ups and cognitive assessments can help identify early signs of cognitive impairment and allow for timely intervention. Healthcare providers can recommend personalized strategies based on individual health profiles, including medication management for chronic conditions that may impact cognitive health. Early diagnosis of conditions such as hypertension or diabetes can lead to effective treatments that mitigate their effects on cognitive function.
In some cases, pharmacological interventions may be necessary to address specific cognitive issues. Research is ongoing into medications that can enhance cognitive function or slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. While there are currently no definitive cures for diseases like Alzheimer's, certain medications may help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Collaborating closely with healthcare providers can ensure that individuals receive the appropriate medical support tailored to their needs.
Additionally, emerging research into supplements and nutraceuticals offers promising avenues for supporting cognitive health. Substances such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and specific vitamins have shown potential in enhancing cognitive function and reducing the risk of decline. However, it is crucial to approach these options with caution and consult healthcare professionals before starting any new supplements. By combining lifestyle modifications with appropriate medical interventions, individuals can create a comprehensive approach to safeguarding their cognitive health and preventing decline.